Diatomic elements are molecules of only two atoms of the same or various chemical aspects. The prefix di- is of Greek origin, suggesting “two”. If a diatomic particle contains two atoms of the same component, such as hydrogen (H2) or oxygen (O2), it is stated to be homonuclear. Or else, if a diatomic particle contains two different atoms, such as carbon monoxide gas (CO) or nitric oxide (NO), the particle is stated to be heteronuclear. The bond in a homonuclear diatomic particle is non-polar.
Diatomic Elements contain two atoms bonded together. In contrast, monatomic components include solitary atoms. Lots of compounds are diatomic, such as HCl, NaCl, and KBr. Diatomic compounds consist of two various elements. Seven pure elements create diatomic Components.
Definition of Diatomic Elements
Major sections make up the earth’s environment: nitrogen, oxygen, and a lot a bit example of argon. To better accuracy, nitrogen composes 78 per cent of the space while oxygen makes up 21%.
As pure components, diatomic components are seven individual particles of two atoms. Every one of the aspects in this honourable group is gases. Suppose we see the prefix ‘di-‘ in words diatomic. In that case, it comes from the Greek beginning of ‘two.’ One effective means to recognize you are operating with a diatomic element is to consider its formula. Every molecule has its one-of-a-kind molecular formula, as well as diatomic components. Their formula routinely contains a supplement of 2, which does two atoms in its setup. For example, the diatomic component oxygen has a formula of O2, implying there are two different oxygen atoms present.
At the area temperature level, there are five diatomic aspects in the gas form: hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen, fluorine, and chlorine. If the temperature level is increased a little greater, two added components will be present: bromine and iodine. At room temperature, bromine and iodine frequently exist in the fluid type. However, keeping that greater temperature level, they will likewise exist as gases.
Few more details
Diatomic aspects are unique as the atoms that form it do not like to be alone. You will indeed never find a nitrogen or fluorine atom, as an example, socializing solo. Instead, these atoms will certainly always be paired since they require merging resources to have adequate electrons. One terrific method to remember which atoms form the lucky seven diatomic aspects is to consider the complying with mnemonic gadget: I Bring Cookies For Our New Residence.
If there is ever a requirement to identify these diatomic aspects on the periodic table, they can be determined by considering the ‘seven regulations’. When drawing the number 7, don’t forget about the 7th element, hydrogen.
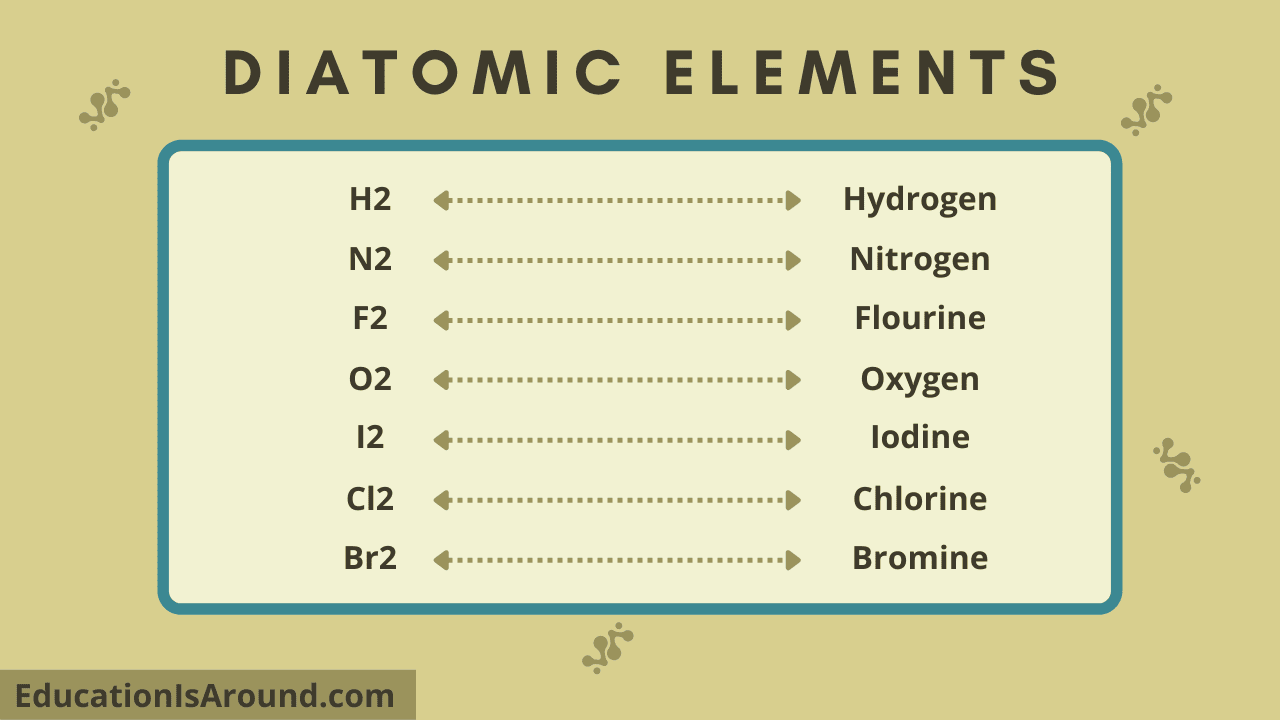
7 Diatomic Elements
This is a list of the seven diatomic elements. The seven diatomic components are:
- Nitrogen (N2).
- Hydrogen (H2).
- Oxygen (O2).
- Chlorine (Cl2).
- Fluorine (F2).
- Bromine (Br2).
- Iodine (I2).
These aspects are nonmetals considering that halogens are a particular sort of nonmetallic element. Bromine is fluid at room temperature, while the other components are gases under stable conditions. As the temperature is decreased or pressure is enhanced, the other members become diatomic liquids. Astatine (atomic number 85, icon At) and Tennessee (atomic number 117, sign Ts) are likewise in the halogen group and may form diatomic particles. However, some researchers predict Tennessee may behave more like a noble gas.
While these seven elements create diatomic molecules, other aspects can make them. Nonetheless, diatomic molecules formed by other factors are not highly steady, so their bonds are conveniently broken.
How To Keep In Mind Diatomic Elements.
There is an easy way to keep in mind the seven diatomic, the “seven guidelines.” First, most likely to aspect seven (Nitrogen), and after that, make a 7 with your finger with oxygen and fluorine, then down through chlorine, bromine, and iodine. That’s 6. The 7th, hydrogen, is the “oddball” of the periodic table, off by itself.
What Are Diatomic Elements?
At the Area Temperature level, There Are Five Diatomic Elements, All Of Which Exist In The Gas Form: Hydrogen, Nitrogen, Oxygen, Fluorine, As Well As Chlorine. If The Temperature Level Is Elevate A Little Higher, Two Add Elements Will Be Present: Bromine And Iodine.
What Are The 7 Diatomic Components?
The 7 Diatomic Components Are:
- Hydrogen (H2).
- Nitrogen (N2).
- Oxygen (O2).
- Fluorine (F2).
- Chlorine (Cl2).
- Iodine (I2).
- Bromine (Br2).
Are Diatomic Elements Compounds?
All Compounds Are Particles, But Not All Molecules Are Substances (If They Take Place To Have Atoms Of The Very Same Aspect). Diatomic Particles Are Molecules Compose Of Only 2 Atoms Of The Exact Same Or Different Components. Nevertheless, not every Diatomic Particle consists of a chemical substance.
How Many Diatomic Aspects Exist?
Seven Components.
7 Aspects Naturally Take Place As Homonuclear Diatomic Particles In Their Gaseous States. Additionally, it includes Hydrogen, Nitrogen, Oxygen, Fluorine, Chlorine, Bromine, and Iodine.
Is Hcl A Diatomic Element?
All Various Other Diatomic Particles Are Chemical Substances Of 2 Various Aspects. Lots Of Components Can Combine To Form Heteronuclear Diatomic Particles, Depending On Temperature And Pressure. Some Instances Include Gases, Carbon Monoxide Gas (Carbon Monoxide), Nitric Oxide (No), And Also Hydrogen Chloride (HCl).